As men age, the risk of developing health conditions like heart disease and type 2 diabetes increases. As daunting as that seems, you can help take control of your health by making healthier food choices.
This article will explore eight men’s most common health issues and how healthier eating can help prevent them.
To better understand what you might be at risk for and which foods will have the biggest impact on your health, take Men’s Health Check. Knowing where you stand can empower you to start making healthier choices today. Let’s dig in.
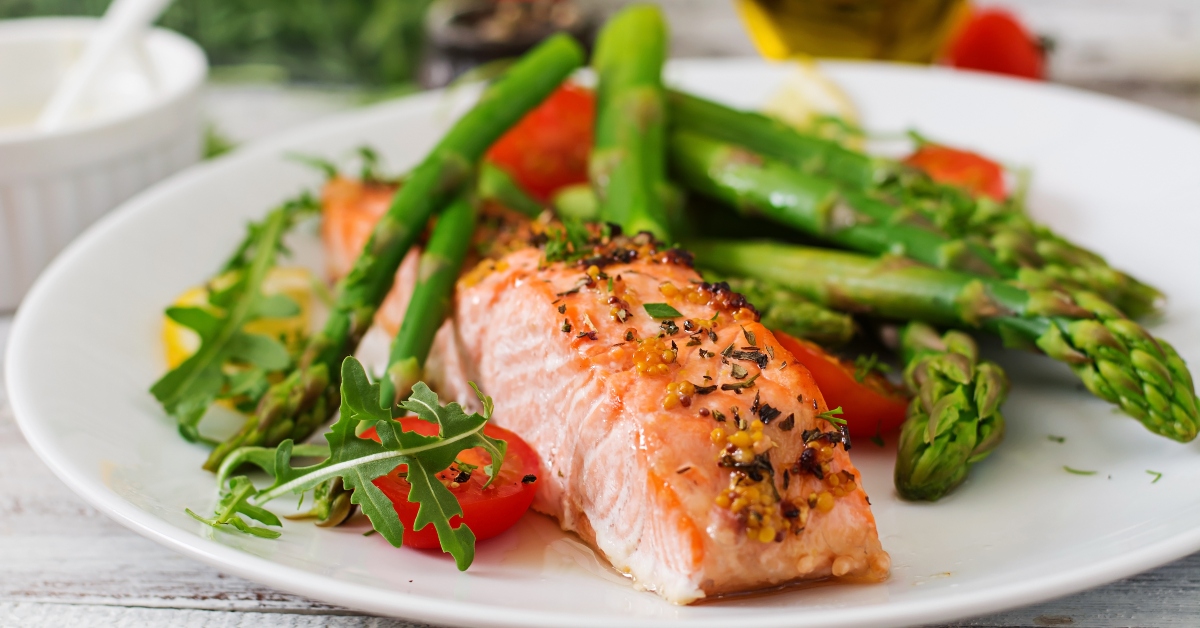
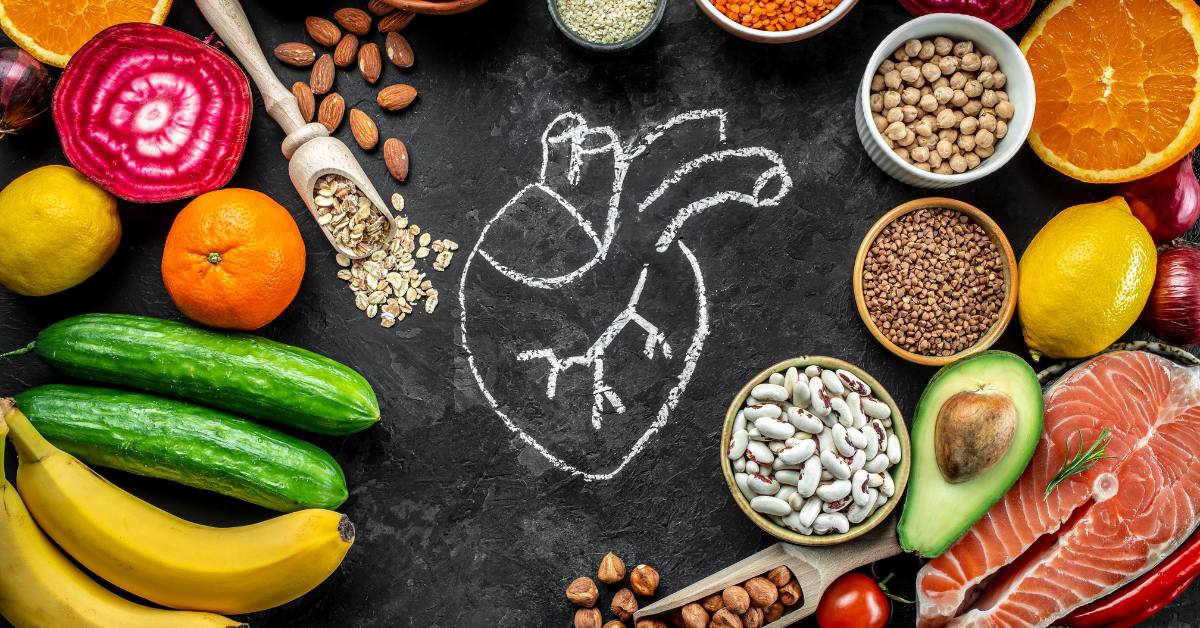
Heart-healthy foods
Men are twice as likely to have a heart attack than women.
Getting enough nutrients like fibre and omega-3 fatty acids may help reduce your risk of developing heart disease.
Examples of heart-healthy foods include:
- Vegetables
- Fruit
- Nuts & seeds
- Beans
- Lentils
- Whole grains
- Fatty fish
- Certain plant-based oils like extra virgin olive oil and avocado oil
Eat less foods high in salt and saturated fat for heart health.
Erectile dysfunction
Erectile Dysfunction (ED) affects roughly 3 million Canadian men over the age of 40. While this may sound concerning, there are steps you can take to lower your risk.
One study reported that men who consumed flavonoid-rich fruits had a 19% reduction in ED incidence. Examples include:
- Apples
- Pears
- Citrus fruits
- Strawberries
- Blueberries
Prostate foods

Prostate cancer is the most common cancer and the third leading cause of cancer deaths among Canadian men. It’s estimated that 5,000 Canadian men will die from prostate cancer in 2024.
A healthy lifestyle, including a nutritious diet, may help reduce your risk.
Eat more fruits & vegetables. Fruits and vegetables high in lycopene–like tomatoes—may help slow cancer cell growth. Cruciferous vegetables–like broccoli–contain a compound known as sulforaphane that may help protect against cancer.
Drink green tea. The antioxidants in green tea may discourage the growth of cancer cells in the prostate.
Low testosterone and diet
Testosterone is a sex hormone responsible for bone formation, muscle growth, producing red blood cells, sex drive and, in males, sperm production.
The risk of low testosterone (also known as Testosterone Deficiency – TD) increases with age and about 25% of men aged 40-62 experience TD. TD can have a variety of symptoms including but not limited to:
- Decreased sex drive
- Sexual dysfunction
- Changes in mood
- Fatigue
While diet is unlikely the direct cause of TD (except in some cases involving anorexia or extreme nutrient deficiencies), there is a link between low testosterone and diet. Certain foods impact testosterone production.
Essential nutrients like zinc, vitamin D, magnesium, and selenium are important for testosterone production, and a deficiency of these nutrients could lead to TD.
Foods high in these nutrients are:
- Nuts & seeds
- Shellfish
- Fatty fish
- Beans
- Lentils
In particular, inflammatory foods may lower testosterone, and according to some research, consuming anti-inflammatory foods like garlic may help boost testosterone levels.
Depression and nutrition connection
There is a connection between diet and depression. One long-term study reported men who consumed high levels of added sugar had an increased risk of developing a mental disorder by 23% after five years.
So what can you do? Following a Mediterranean diet, which is typically low in added sugars, may help improve symptoms of depression.
While dietary changes may help improve symptoms, always work with a healthcare professional to determine the best form of treatment for you.
Colorectal cancer and diet
Colorectal cancer is the second leading cause of death from cancer in men. Specifically, about 1 in 16 men will get colon cancer, and 1 in 38 will die from it.
So, what can you do to reduce your risk? Foods high in fibre help bulk stool move more quickly through the digestive system and decrease the risk of developing colon cancer. Foods high in fibre include:
- Vegetables
- Fruits
- Beans & lentils
- Grain products
Limiting certain foods like processed or red meats is also beneficial. These foods can develop cancer-causing compounds when cooked at high temperatures.
Type 2 diabetes and prevention
Men are at a greater risk of developing type 2 diabetes than women. Certain populations are also more at risk, including First Nations, African, Arab, Asian, Hispanic and South Asian populations.
Whole plant foods, lean meats, and heart-promoting fats help delay the onset and reduce risk because they are high in fibre, which helps moderate blood sugar levels.
Limiting foods high in salt, saturated fat, and added sugars may also help delay the onset or decrease the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Osteoporosis diet

The risk of developing osteoporosis increases with age. In fact, according to Osteoporosis Canada, one in five men with osteoporosis will break a bone.
Three essential nutrients play a vital role in osteoporosis prevention:
- Protein
- Calcium
- Vitamin D
Protein
Vital for muscle and bone growth and repair.
Protein needs for men vary depending on age, activity level, and the presence or absence of chronic disease. However, typically, making ¼ of your plate a lean protein is an excellent place to start. Here are some examples:
- Chicken breast
- Fatty fish (salmon, tuna, mackerel, rainbow trout)
- Eggs
- Greek yogurt
- Tofu
- Beans & lentils
- Lentils
- Nuts & seeds
Calcium
Essential for building and maintaining bones.
The calcium needs of men aged 19-70 are 1000 mg daily, which is about three servings of calcium-rich foods. As you age, your calcium needs increase, and men over 71 need 1200 mg daily or about four servings.
Here are some examples of serving sizes of calcium:
- 1 cup dairy milk
- 1 cup fortified plant-based milk
- 1 cup cottage cheese
- ¾ cup Greek yogurt
- 150 g fortified tofu
- 100 g canned salmon with bones
Vitamin D
Helps the body absorb calcium.
Vitamin D recommendations for men of any age are 400 IU daily. Your body can make vitamin D from the sun during the summer months; however, it makes very little, if any, during the winter months. This is why getting your vitamin D from food and possibly even a supplement is recommended.
Food sources of vitamin D include:
- Dairy milk
- Fortified plant-based milk
- Eggs
- Certain types of fish (particularly ones with bones like canned salmon)
From heart disease to low testosterone, a balanced diet plays a crucial role in prevention. Focus on nutrient-rich options to help reduce your risk of developing these common men’s health conditions.
Start by assessing your risk with the Men’s Health Check and take charge of your health today. Small changes now can lead to big benefits down the road.
Has making healthier diet choices impacted your health? If so, we’d love to hear your story! Let us know in the comments below or email us at [email protected].
Are You at Risk?
Learn your risk level for the most common men’s health conditions in 10 minutes with a free, confidential, and personalized report.





Great article. I’ve adapted my lifestyle to a Mediterranean focused diet and it’s shown results. Hopefully more men listen to this advice as it’s beneficial to all for a healthy progression through life.